At Joyin we are specialized in early communication interventions for children who are late in their speech production.
The intervention is designed to help children to produce more frequent and more complex communication in the form of gestures, sounds and words. The intervention is individualized to each child and is appropriate for children ranging from prelinguistic to those with emerging language
WHO CAN BENEFIT?
The intervention is intended for:
- children with speech delay
- children with generalized developmental delays
- children with or at risk or Autism
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
We adopt a naturalistic, relation-based intervention that uses child initiations and natural interactions as opportunities to develop speech and language.
Research shows that naturalistic approaches to speech delays are more effective in generating functional and generalized communication when compared with drill-practice methods, where the child is taught language outside of its relational and pragmatic context (for example at the table using flashcards, see Yoder, Kaiser et Alpert, l991, Kaiser, Yoder, et al,1996).
The therapeutic approach we implement has shown evidence of efficacy in:
- Developing child intentional communication, sound and word production (Scherer & Kaiser, 2010; Roberts & Kaiser, 2012; Kaiser & Roberts, 2012);
- Increasing child frequency and complexity of communication (Warren et al, 1994; Kaiser et al, l993)
- Generalizing communicative targets across settings and people (Kaiser & Roberts , 2012).
Areas of intervention and strategies
The contemporary scientific view on language acquisition recognizes the importance of prelinguistic interactions as a foundation for spoken word production. Consequently, it is crucial for clinical treatments for speech delay to adopt a comprehensive approach to facilitate the acquisition of prerequisite and related skills that are essential to the development of spoken communication.
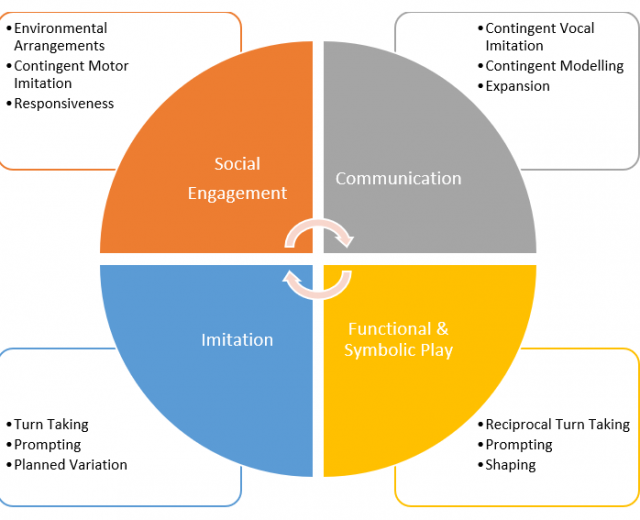
The strategies implemented in our interventions (see figure) aim to:
- Increase duration and quality of social engagement with others
- Develop age appropriate functional and symbolic play
- Increase frequency of imitation
- Increase comprehension and production of prelinguistic and linguistic communication